WJEC Eduqas GCE AS Level Unit 1 (from 2015 onwards)
|
Summary Presentation of all the elements of Component 1 - this is hosted by me but edited completely by my students using resources they have found, sourced or in a couple of cases written.
|
1.1 Biological Molecules
A biomolecule is any molecule that is produced by a living organism, including large macromolecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, and nucleic acids
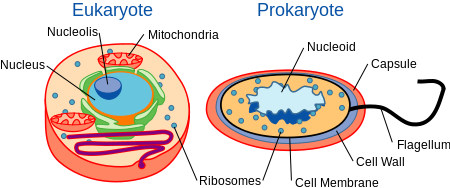
1.2 Cell Structure
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing
1.3 Membranes
A biological membrane is an enclosing membrane that acts as a selective barrier, within or around a cell. It consists of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins
1.4 Enzymes
Enzymes are large biological molecules (proteins) that are responsible for catalysing the thousands of chemical inter-conversions that sustain life
1.5 Industrial Use of Enzymes
Enzymes (above) are used in the chemical industry and other industrial applications when extremely specific catalysts are required.
1.6 Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are large biological molecules essential for all known forms of life. They include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid).
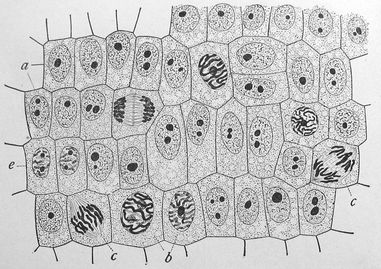
1.7 Cell Division
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the cell contents into two cells containing roughly equal shares of the cellular components
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||